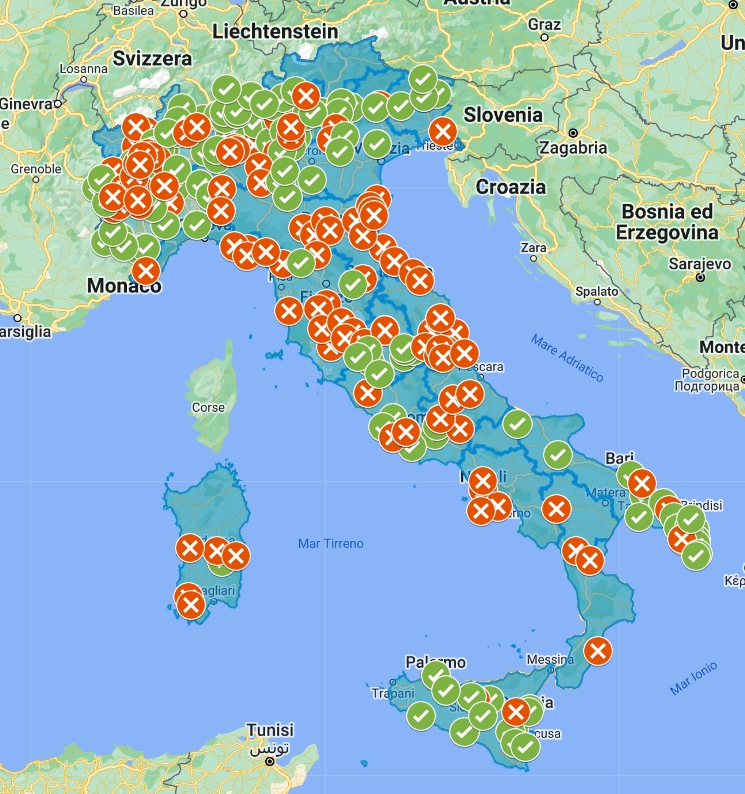
Survey and atlas of italian ecomuseums
November 23, 2022 in
In 2017 a census was carried out which surveyed about 200 Italian institutions that define themselves as ecomuseums. Only a part of these are recognized by the regional legislation on ecomuseums.
The census was updated in 2021 and 2022.
The Atlas shows the 264 Italian cultural institutes that define themselves as ecomuseums (2022 update on Damia data, 2017). The project is nearing completion. Additions by interested stakeholders are welcome. Open the interactive map to learn about the characteristics of the surveyed ecomuseums.
151 Ecomuseums are recognized by laws, 130 is part of regional networks, 50 developed one or more parish map to survey the living heritage.
More at: https://sites.google.com/view/ecomuseiitaliani/chi-siamo

Distant but United: the Ecomuseums and community museums of Italy and Brazil
November 23, 2022 in
In 2020, Brazil and Italy were among the countries most adversely affected by the Covid-19 pandemic. The situation highlighted latent structural crises at social and economic levels and prompted widespread concern for the future. Operating in this context, ecomuseums and community museums continued their mission of caring for and interpreting living cultural heritage, empowering communities to sustainably manage heritage and thus contributing to integral local development and the strengthening of a shared social consciousness and identity. Measures aiming at the containment of the pandemic led ecomuseums to explore new methods of public engagement, inspiration and support in a bid to meet local community needs.
The Brazilian Association of Ecomuseums and Community Museums (ABREMC) and the Italian Ecomuseums Network (EMI) discussed and approved the cooperation charter ‘Distant but United. The Ecomuseums and Community Museums of Italy and Brazil’ over the course of several meetings, reflecting on the responsibilities of museums in a period of crisis. The charter identifies the 10-year commitments of the signatories for the implementation of an articulated cooperation programme, as well as defining an annual calendar of promoted actions. It lays out agreed themes and strategic lines (Exchanging, Welcoming, Publishing, Training, Inviting, Organising, Communicating, and Monitoring), as well as implementation times and actions to be carried out with the involvement of actors from both sides.
The charter stresses the role of ecomuseums and community museums in the promotion of both museum practices and a transition towards the creation of resilient communities, supporting them towards the goal of renewing themselves and facing contemporary crises in effective and sustainable ways. This article presents the main themes and objectives of the charter and proposes a theoretical model for understanding how bolstering communities and their ‘social imaginaries’ is crucial to fostering the integral development of communities and social innovation. It first discusses the changes necessary to overcome contemporary crises by drawing on some important theoretical models; before turning to examine how ecomuseums of Italy and Brazil responded to limitations imposed by the Covid-19 pandemic. It next presents a few ecomuseum practices developed during the pandemic, illustrates the methodology and contents of the charter and, finally, presents the main results, limitations and development prospects of the cooperation experience.
More at this link
